ISO 13485 certification in DURBAN
Get Free Consultation
PopularCert is your trusted partner for ISO 13485 certification in Durban, helping businesses in the medical device industry achieve compliance with international quality standards. Our expert consultants provide end-to-end support, from gap analysis and documentation to implementation and audit preparation. With PopularCert, you can streamline your certification journey, enhance product quality, and demonstrate your commitment to patient safety. Let us help you build trust with stakeholders, expand into new markets, and gain a competitive edge with ISO 13485 certification.
What is ISO 13485 Certification?
ISO 13485 is an international standard for Quality Management Systems (QMS) specifically for the medical device industry. It outlines requirements for organizations involved in the design, production, installation, and servicing of medical devices. The certification ensures that a company meets regulatory requirements and consistently produces safe, effective, and high-quality medical devices. ISO 13485 focuses on risk management, product traceability, and maintaining consistent processes to improve product quality. Achieving ISO 13485 certification demonstrates a commitment to patient safety and regulatory compliance, fostering trust among customers and stakeholders while enhancing operational efficiency and market access for medical device manufacturers.
Why ISO 13485 Certification Matters in Durban?
Durban’s medical device industry is growing fast, and ISO 13485 certification plays a key role in ensuring quality and safety. It helps businesses create reliable and effective medical devices while meeting all the necessary regulations. This certification shows that a company is serious about protecting patient safety, boosting customer confidence, and standing out in the market.
By getting ISO 13485 certified, businesses in Durban can also improve their processes, reduce waste, and run more efficiently. Plus, it opens the door to global markets, giving them a chance to compete on an international level and establish themselves as trusted leaders in healthcare.
How to Get ISO 13485 Certification In Durban?
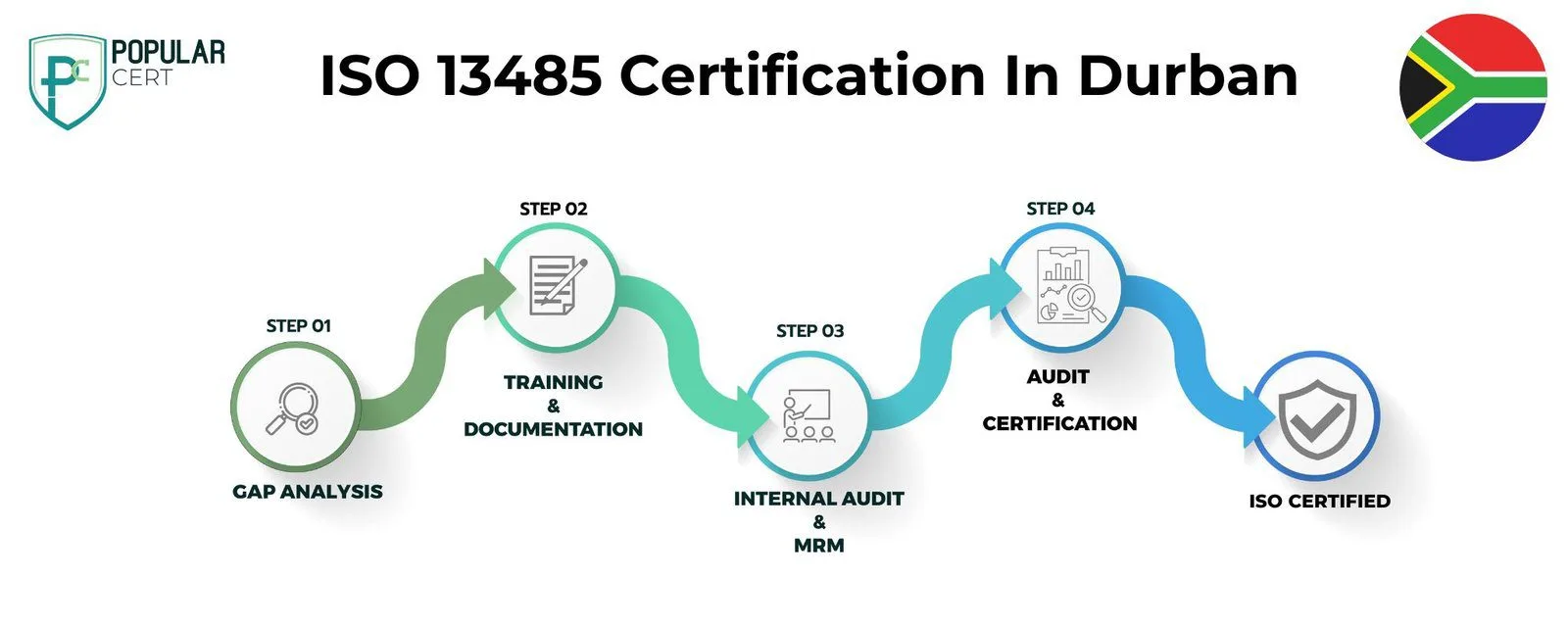
Process to Get ISO 13485 Certification In Durban
Consultation and Gap Analysis
PopularCert’s specialists assess your organization’s specific requirements and existing systems. We conduct a thorough gap analysis to pinpoint areas needing improvement to meet ISO standards.
Planning, Documentation, and Policy Development
Following the gap analysis, we create a customized implementation plan, define resource needs, and assist in developing necessary policies and documentation. These are seamlessly integrated into your current organizational framework.
Training and Awareness
Comprehensive training ensures your team understands ISO requirements and their responsibilities in maintaining the management system effectively.
Internal Audit and Management Review
We perform internal audits to evaluate system effectiveness and address any non-conformities. A management review aligns the system with your organization’s objectives and ISO standards.
External Certification Audit and Certification
After successfully completing the external audit, your organization will earn ISO certification. This reflects your commitment to excellence, strengthens credibility, and builds lasting trust with customers and stakeholders.
Benefits Of ISO 13485 Certification In Durban
- Improved Quality Management: ISO 13485 helps businesses create a reliable system for maintaining high-quality standards in their products, ensuring they meet both customer and regulatory requirements.
- Increased Market Access: Certification allows companies to expand into new markets by meeting international regulatory standards, making it easier to sell medical devices globally.
- Better Risk Management: The certification focuses on reducing risks associated with medical device production by setting procedures for identifying and mitigating potential issues.
- Enhanced Customer Confidence: Achieving ISO 13485 signals to customers that the company prioritizes quality and safety, improving trust and customer loyalty.
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: It ensures that your medical devices meet all necessary legal and regulatory standards in Durban and other regions, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Continuous Improvement: ISO 13485 emphasizes continual improvement, encouraging companies to regularly assess their processes and products to ensure ongoing compliance and better performance.
Types Of ISO Certification In Durban
Get Free Consultation
Our Clients


















Why do you need ISO 13485 Certification in Durban?
ISO 13485 certification is crucial for businesses in Durban involved in manufacturing, designing, or distributing medical devices. It ensures compliance with both local and international regulations, which is essential for accessing global markets and meeting the growing demand for high-quality, safe medical products. Achieving ISO 13485 certification demonstrates a commitment to product quality, regulatory adherence, and continuous improvement. It helps businesses improve operational efficiency, reduce risks, and enhance customer satisfaction.
In Durban’s competitive healthcare and medical device sector, ISO 13485 certification not only improves credibility but also strengthens relationships with customers, regulatory bodies, and stakeholders. It positions businesses to thrive in the evolving medical device industry.
Cost Of ISO 13485 Certification In Durban
The cost of ISO 13485 certification in Durban depends on factors such as the size of the organization, the complexity of operations, and the scope of certification. Costs typically cover gap analysis, documentation preparation, employee training, internal audits, and certification body fees. To get a precise cost estimate, it’s recommended to consult with a certification provider like PopularCert, who can assess your organization’s specific requirements and offer a tailored, cost-effective solution for ISO 13485 certification. For more information and to apply for your ISO 13485 Certification In Durban, We will guide you through the process and provide details on the cost involved to help you get started on your ISO Certification journey with PopularCert in Durban.
Why Choose PopularCert For ISO 13485 Certification In Durban?
PopularCert offers over 10 years of experience in ISO certifications, specializing in sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and technology. Our expert consultants provide personalized guidance through every stage of certification, ensuring compliance with international standards. We prioritize quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, helping businesses in Durban achieve ISO 13485 and other certifications with minimal disruption. Choose PopularCert for a seamless certification process and a trusted partner in achieving operational excellence and market competitiveness.
GET A FREE CONSULTATION NOW
FAQ
What is ISO 13485 and why is it important for businesses in Durban?
ISO 13485 is a global standard for quality management systems in the medical device industry. It ensures regulatory compliance, product safety, and quality. For businesses in Durban, it enhances credibility, improves customer trust, and provides access to global markets.
How can my organization achieve ISO 13485 certification in Durban?
To achieve ISO 13485 certification in Durban, your organization must implement a quality management system that meets the standard’s requirements. This involves conducting a gap analysis, documenting procedures, training staff, conducting internal audits, and addressing non-conformities. Finally, an accredited certification body will conduct an external audit for certification.
How does PopularCert assist in obtaining ISO 13485 certification?
PopularCert assists in obtaining ISO 13485 certification by providing expert guidance through the entire process. This includes gap analysis, documentation support, training, internal audits, and preparing your organization for the final external audit, ensuring a smooth and efficient certification journey.
How long does it take to get ISO 13485 certification in Duban with PopularCert?
The time to achieve ISO 13485 certification in Durban with PopularCert typically ranges from 3 to 6 months, depending on your organization’s size, complexity, and readiness. PopularCert ensures a streamlined process by providing tailored support throughout each step.
