ISO 13485 certification in MOMBASA
Get Free Consultation
PopularCert helps businesses stay ahead by offering ISO 13485 Certification in Mombasa, essential for medical device manufacturers. As Mombasa grows into a key trade hub, this certification ensures companies meet global standards for quality management in the design and production of medical devices.
ISO 13485 demonstrates a company’s commitment to delivering safe, reliable products, building customer trust and opening doors to international markets. With Kenya’s expanding economy, ISO 13485 Certification helps businesses improve operations, comply with regulations, and stand out in a competitive industry, setting them up for long-term success.
Why ISO 13485 Certification is important for you and your business in Mombasa.
ISO 13485 is crucial for medical device companies in Mombasa to ensure their products are safe, reliable, and meet strict regulatory requirements. This certification helps businesses reduce risks, enhance processes, and deliver high-quality devices that customers can trust.
By obtaining ISO 13485 certification, companies demonstrate their commitment to quality, improve their reputation, and gain access to global markets. It enables organizations to meet international standards, increase operational efficiency, and enhance patient safety, ultimately driving long-term success.
How to Get ISO 13485 Certification in Mombasa?
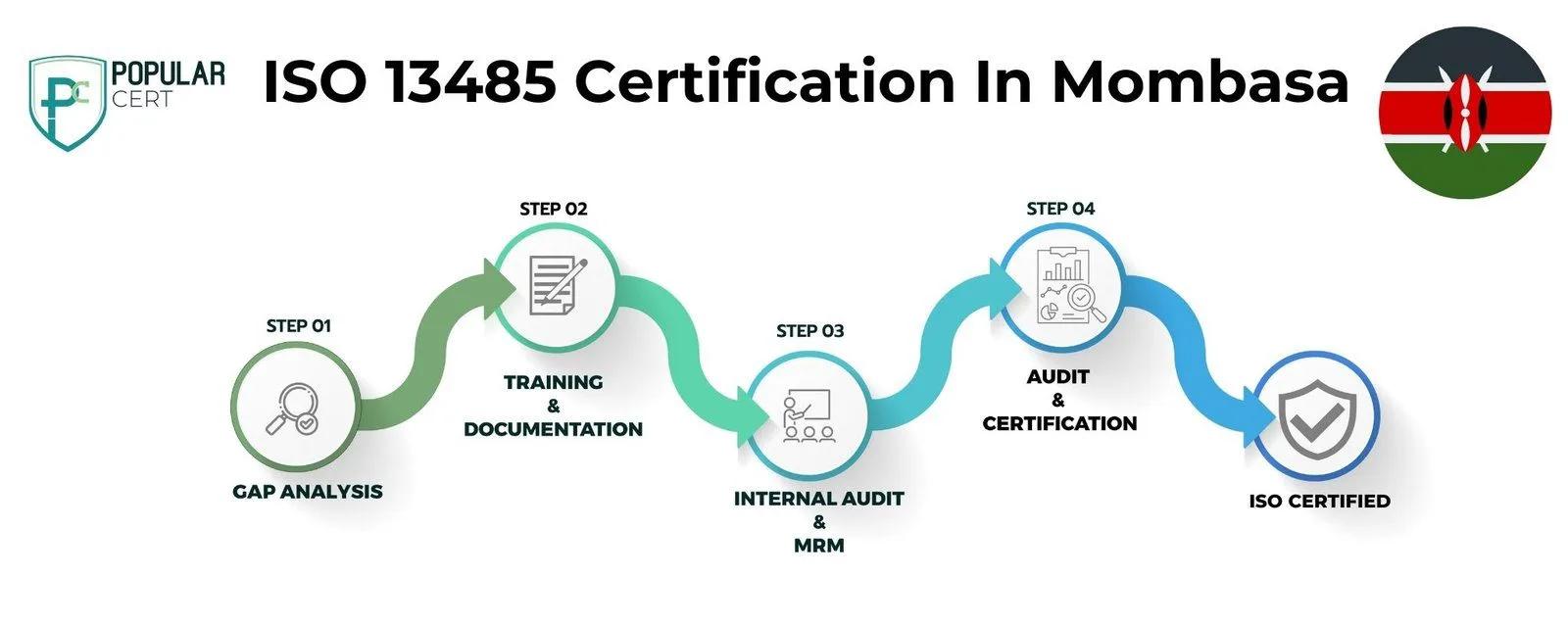
Process to Get ISO 13485 Certification In Mombasa
Consultation and Gap Analysis
PopularCert’s experts begin by understanding your organization’s needs and current management practices in Mombasa. We then conduct a gap analysis to identify areas requiring improvement to achieve ISO 13485 certification, ensuring your organization is well-prepared to meet international standards for medical devices. This comprehensive approach guarantees that your business is on the right path to enhance quality, efficiency, and compliance, while ensuring the safety and reliability of your medical devices.
Planning, Documentation, and Policy Development
Based on the gap analysis, we develop a detailed implementation plan for your organization in Mombasa, allocate resources, and assist in creating essential policies and documentation required for ISO 13485 certification. These policies and procedures are seamlessly integrated into your existing framework, ensuring compliance with medical device regulations and effective implementation of ISO 13485 standards. This tailored approach ensures a smooth transition towards achieving certification while enhancing operational efficiency, improving quality management, and ensuring the safety and reliability of your medical devices.
Training and Awareness
We provide comprehensive training for your staff in Mombasa, ensuring they understand the requirements of ISO 13485 certification and their role in effectively implementing and maintaining the medical device quality management system. Our training programs are tailored to meet the specific needs of your organization, empowering your team to successfully achieve and sustain ISO 13485 certification. This approach ensures that your staff is equipped with the knowledge and skills needed for continuous improvement, patient safety, and compliance with international standards in the medical device industry.
Internal Audit and Management Review
After implementing the ISO 13485 management system, we conduct an internal audit in Mombasa to assess its efficiency and identify any non-conformities specific to the medical device industry. Following this, a management review is carried out to ensure the system aligns with your organization's goals and regulatory compliance requirements, ensuring readiness for ISO 13485 certification. This process guarantees that your organization is fully prepared, compliant, and committed to continuous improvement, setting the stage for a successful external audit and certification.
External Certification Audit and Certification
After successfully completing the external audit by the certification body, your organization in Mombasa will be awarded ISO 13485 certification. This certification highlights your commitment to high standards in medical device quality management and continuous improvement. It demonstrates your dedication to ensuring product safety and regulatory compliance, enhancing your credibility and building trust with customers, regulators, and stakeholders. Achieving ISO 13485 certification positions your organization as a leader in quality and patient safety, boosting your reputation and opening doors to new growth opportunities in global markets.
Benefits of ISO 13485 Certification in Mombasa
- Regulatory compliance : ISO 13485 aligns with the regulations and standards set by Mombasa’s healthcare bodies, ensuring compliance with local and international healthcare requirements. Adhering to the ISO 13485 standard helps organizations navigate complex regulatory landscapes, improving their ability to meet both local and global standards, and enhances their credibility in the medical device industry.
- Market access : Having ISO 13485 certification helps your organization gain access to the Mombasa market and beyond. It demonstrates that you follow international quality standards, giving you a competitive edge when bidding for contracts and ensuring compliance with local health and safety regulations. This certification enhances your credibility, making it easier to build trust with clients and partners.
- Improved product quality : The ISO 13485 standard calls for strict checks and steps in all stages of a product's life, from creation to production and beyond to customer feedback. This leads to better healthcare devices and a lower chance of issues, making patients safer and happier.
- Risk management : ISO 13485 focuses on managing and lessening risks during the device's lifespan. Spotting concerns early can stop minor issues from growing into serious problems. This decreases the chances for expensive recalls and legal difficulties.
- Operational efficiency : Putting ISO 13485 to work helps make processes smooth and constantly better. Companies see perks like sharper operations, less waste and smarter handling of resources. This can cut costs and boost earnings.
- Increased credibility and trust : Earning a certification proves your dedication to excellence and safety. It is a great way to earn trust from important people like customers, regulatory bodies and partners. It boosts your organization's reputation in the market.
Types Of ISO Certification In Mombasa
Get Free Consultation
Our Clients


















Cost of ISO 13485 Certification in Mombasa
The cost of ISO 13485 certification in Mombasa depends on factors such as the size of the organization, the complexity of its quality management system, and its current level of compliance with medical device regulations. Typical expenses include gap analysis, training, documentation preparation, audits, and implementation support. PopularCert offers tailored and cost-effective solutions to help businesses in Mombasa achieve ISO 13485 certification, ensuring compliance with international standards for medical devices and enhancing operational efficiency, product quality, and regulatory compliance.
Why Choose PopularCert For ISO 13485 Certification in Mombasa?
PopularCert is a globally renowned consulting company specializing in certification, advisory, and auditing services. We are the trusted choice for organizations seeking ISO 13485 certification in Mombasa due to our experienced, ethical consultants and proven success record. For ISO 13485 certification in Mombasa, choose PopularCert, a leader in consultancy, certification, and auditing services.
