Simple Guide to Monitoring, Compliance & Safety in Your Workplace – AS/NZS & OHSAS Made Easy

Creating a safe and healthy workplace isn’t just about wearing helmets or putting up signs. It’s about regularly checking how your safety systems are working, fixing what’s not, and always staying ahead of risks. Here’s a simplified overview of what organizations should do under AS/NZS and OHSAS standards to ensure occupational health and safety (OH&S).
AS/NZS Monitoring and measurement/OHSAS Performance measurement and monitoring
The organisation shall establish and maintain procedures to monitor and measure the key characteristics of its operations and activities that can cause illness and injury on a regular basis. These procedures shall provide for:
- Both qualitative and quantitative measures, appropriate to the needs of the organization
- Monitoring to the extent to which the organization’s OH&S objectives are met
- Monitoring the effectiveness of Controls
- Proactive measures of performance that monitor conformance with the OH&S programmes, controls and operational criteria.
- Reactive measures of performance that monitor ill health, incidents and other historical evidence of deficient OH&S performance.
- Recording of data and results of monitoring and measurement.
Monitoring and Measurement
Monitoring Equipment
- For the appropriate monitoring equipment related to health and safety risks, the organization shall establish and maintain procedures for the calibration and maintenance of such equipment.
- Calibration frequency shall be determined for the equipment.
- Records of calibration and maintenance activities and results shall be retained.
Health surveillance
- The organisation shall identify those situations where employee health surveillance is required and shall implement appropriate systems.
- Where specified by the legislation, the health of employees exposed to hazards shall be monitored and recorded.
- Employees shall have access to their own.
Why Health surveillance
Possible effect in case of omission: Health hazard to Employees. The organization will not be able to determine/identify any health changes that may be due to the occupational exposure to a hazard by an Individual who might be affected by it.
What to look for as an auditor
- A procedure in place for monitoring health of employees who are exposed to specific hazards.
- Verify Records of such results.
- Verify the privacy of the records is maintained.
- Verify for any specified legislative requirements applicable to the organization.
- They shall be periodically verified to ensure accuracy of results.
Types Of Certification
- ISO Certification
- ISO 9001 Certification
- ISO 14001 Certification
- ISO 45001 Certification
- ISO 22000 Certification
- ISO 27001 Certification
- ISO 17025 Certification
- ISO 13485 Certification
- ISO 20000-1 Certification
- ISO 22301 Certification
- ISO 50001 Certification
- ISO 37001 Certification
- IATF 16949 Certification
- ISO 29001 Certification
- ISO 31000 Certification
- ISO 20121 Certification
- ISO 10002 Certification
- ISO 41001 Certification
Get Free Consultation
Our Clients


















OHSAS Evaluation of Compliance
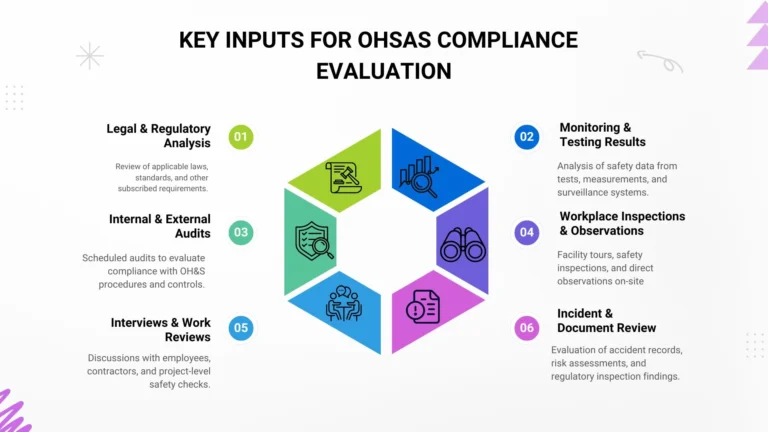
An organization should establish, implement and maintain a procedure for periodically evaluating its compliance with the legal or other requirements that are risks, as part of its commitment to compliance.
Evaluation of the organization’s compliance should be performed by competent persons, either from within the organization and/or using external resources applicable to its OH&S
A variety of inputs can be used to assess compliance, including
- Analysis of legal and other requirements,
- Analysis of test results from monitoring and testing.
- Audits,
- Facility tours and/or direct observations.
- Facility, equipment and area inspections
- Interviews,
- Project or work reviews.
- Reviews of documents and/or records of incidents and risk assessments,
- The results of regulatory inspections,
The organization’s processes for the evaluation of compliance can depend on its nature (size. structure and complexity). A compliance evaluation can encompass multiple legal requirements or a single requirement. The frequency of evaluations can be affected by factors such as past compliance performance or specific legal requirements. The organization can choose to evaluate compliance with individual requirements at different times or at different frequencies, or as appropriate.
A compliance evaluation programme can be integrated with other assessment activities These can include management system audits, environmental audits or quality assurance checks. Similarly, an organization should periodically evaluate its compliance with other requirements to which it subscribes.
An organization can choose to establish a separate process for conducting such evaluations or it can choose to combine these evaluations with its evaluations of compliance with legal requirements, its management review process or other evaluation processes.
The results of the periodic evaluations of compliance with legal or other requirements need to be recorded.
AS/NZS Incident corrective and preventive action OHSAS 453 Incident investigation, non conformity, corrective and preventive action
The organisation shall establish and maintain procedures for defining responsibility and authority for the handling and investigation of
- Accidents
- Incidents
- Non-conformances
and taking action to mitigate any consequences arising from accidents, incidents or non- conformances
Any corrective or preventive action taken to eliminate the causes of actual and potential non-conformances shall be appropriate to the magnitude of problems and commensurate with the OH&S risk encountered.
Implement and record any changes in the documented procedures resulting from corrective and preventive action
What to look for as an auditor
- A procedure in place for monitor
- Written Procedures
- Defined responsibilities/authorities/requirements
- Requirement to report
- Immediate investigation to determine the root cause (who, what, when).
- Record any changes in the OHSMS procedures and inform all interested party of any changes being made.
- Corrective actions and Follow-up
- Classification/Analysis/Communication
- Management involvement/review/input
- Link to change management/hazard identification/risk control
- ing health of employees who are exposed to specific hazards.
- Verify Records of such results.
- Verify the privacy of the records is maintained.
- Verify for any specified legislative requirements applicable to the organization.
- They shall be periodically verified to ensure accuracy of results.
AS/NZS Records and Records Management/OHSAS Control of Records
The organisation shall establish and maintain procedures for the identification, maintenance and disposition of records, as well as the results of audits and management reviews.
- Records shall be legible, identifiable and traceable to the activities involved.
- OH&S records shall be stored and maintained in such a way that they are readily retrievable and protected against damage, deterioration or loss.
- Their retention times shall be established and recorded.
- Records shall be maintained, as appropriate to the system and to the organization, to demonstrate conformance to the specified criteria (e.g., OHSAS 18001).
- Main criteria for determining which records are to be kept:
- Legislative requirements
- Management system requirements
What to look for as an auditor
The procedure should identify:
- Which records are to be kept
- Who is responsible
- Manner of keeping records
- Retention times, etc.
AS/NZS OHSMS Audit
The organisation shall establish and maintain an audit program and procedures for periodic OH&S management system audits to be carried out, in order to determine whether or OH&S management system:
- Conforms to planned arrangements for OH&S management including the requirements of not the specification (e.g., OHSAS 18001)
- Has been effectively implemented and maintained: and
- Is effective in meeting the organization’s policy and objectives
- Provide information on the results of audits to management.
The audit program, including any schedule, shall be based on the results of risk assessments of the organization’s activities, and the results of previous audits
The audit procedures shall cover the scope, frequency, methodologies and competencies, as well as the responsibilities and requirements for conducting audits
Selection of auditors and conduct of audits shall ensure objectivity and impartiality of the and reporting results audit process.
What to look for as an auditor
- Documented procedure for OHSMS Audit
- Audit reporting typical outputs include:
- Audit plan/program
- Audit reports (non-conformance reports, recommendations and corrective action requests)
- Non-conformance reports
- Evidence of reporting results of OH&S management system audit to management
Management Review
- Top management shall, at intervals that it determines, review the OH&S management system, to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy and effectiveness.
- The management review process shall ensure that the necessary information is collected to allow management to carry out this evaluation. This review shall be documented.
- The management review shall address the possible need for changes to policy, objectives and other elements of the OH&S management system, in light of the OH&S management system audit results, changing circumstances and the commitment to continual improvement.
Input to management review shall include
Results of internal audits and evaluation of compliance with legal and other requirement
- The results of participation and consultation
- Relevant communication from external parties including complaints
- OH&S performance
- The extent to which objectives have been met
- Status of investigation, corrective and preventive actions. Follow up actions from the previous management reviews
- Changing circumstances
- Recommendations from improvement
What to look for as an auditor
- Are management reviews conducted at intervals as determined by the organisation?
- Minutes of meeting
- Revisions to OH &S policy and objectives
- Specific corrective actions with target dates and responsibilities Specific improvements with target dates and responsibilities
- Time frame for completion of corrective actions
- Area of emphasis for future planning
Conclusion
Following safety standards like AS/NZS and OHSAS isn’t just about ticking boxes — it’s about protecting people. With the right systems in place, you can spot issues early, fix problems fast, and create a workplace where safety is a habit, not a hassle.
